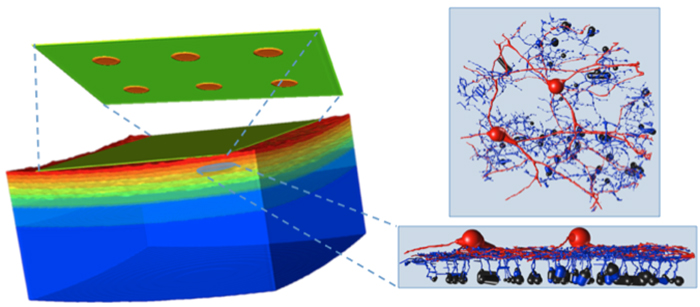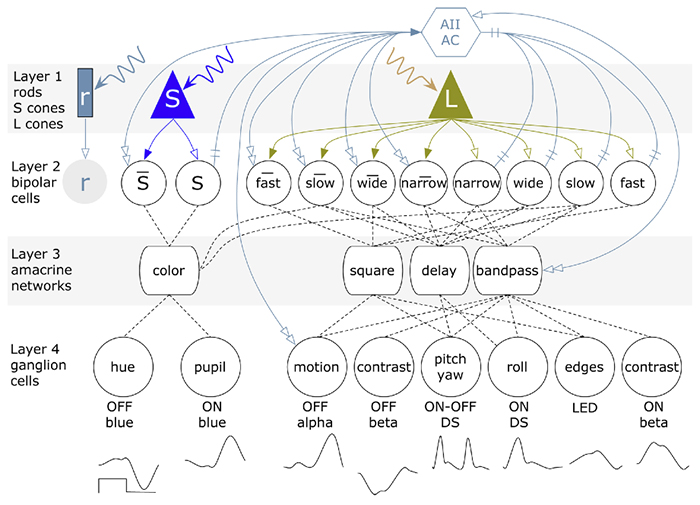
We have a new publication, Retinal Prosthetics, Optogenetics and Photoswitches in ACS Chemical Neuroscience. Authors are: Robert E. Marc, Rebecca L. Pfeiffer, and Bryan W. Jones.
Abstract:
Three technologies have emerged as therapies to restore light sensing to profoundly blind patients suffering from late-stage retinal degenerations: (1) retinal prosthetics, (2) optogenetics, and (3) chemical photoswitches. Prosthetics are the most mature and the only approach in clinical practice. Prosthetic implants require complex surgical intervention and provide only limited visual resolution but can potentially restore navigational ability to many blind patients. Optogenetics uses viral delivery of type 1 opsin genes from prokaryotes or eukaryote algae to restore light responses in survivor neurons. Targeting and expression remain major problems, but are potentially soluble. Importantly, optogenetics could provide the ultimate in high-resolution vision due to the long persistence of gene expression achieved in animal models. Nevertheless, optogenetics remains challenging to implement in human eyes with large volumes, complex disease progression, and physical barriers to viral penetration. Now, a new generation of photochromic ligands or chemical photoswitches (azobenzene-quaternary ammonium derivatives) can be injected into a degenerated mouse eye and, in minutes to hours, activate light responses in neurons. These photoswitches offer the potential for rapidly and reversibly screening the vision restoration expected in an individual patient. Chemical photoswitch variants that persist in the cell membrane could make them a simple therapy of choice, with resolution and sensitivity equivalent to optogenetics approaches. A major complexity in treating retinal degenerations is retinal remodeling: pathologic network rewiring, molecular reprogramming, and cell death that compromise signaling in the surviving retina. Remodeling forces a choice between upstream and downstream targeting, each engaging different benefits and defects. Prosthetics and optogenetics can be implemented in either mode, but the use of chemical photoswitches is currently limited to downstream implementations. Even so, given the high density of human foveal ganglion cells, the ultimate chemical photoswitch treatment could deliver cost-effective, high-resolution vision for the blind.