This poster was presented today, July 28th at the 2019 International Gap Junction Conference in Victoria, Canada by Crystal L. Sigulinsky, Rebecca L. Pfeiffer, James R. Anderson, Christopher Rapp, Jeebika Dahal, Jessica C Garcia, Jia-Hui Yang, Daniel P. Emrich, Hope Morrison, Kevin D. Rapp, Carl B. Watt, Mineo Kondo, Hiroko Terasaki, Robert E. Marc and Bryan W. Jones.
Almost full resolution version here.
Authors:
Crystal L Sigulinsky1, Rebecca L Pfeiffer1, James R. Anderson1, Christopher N. Rapp1, Jeebika Dahal1, Jessica C Garcia1, Jia-Hui Yang1, Daniel P. Emrich1, Hope Morrison1, Kevin D. Rapp1, Carl B. Watt1, Mineo Kondo2, Hiroko Terasaki3, Robert E. Marc1, Bryan W. Jones1
1Moran Eye Center/ Ophthalmology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, United States; 2Mie University, Tsu, Japan; 3Nagoya University, Nagoya-shi, Japan;
ABSTRACT:
Background and aim:
Gap junctions are prevalent throughout the neural retina, with expression by every major neuronal class and at every level of signal processing. Yet, the functional roles and expressing cells/participating networks for many remain unknown. Spontaneous network spontaneous hyperactivity observed during retinal degeneration contributes to visual impairment and requires gap junctional coupling in the Aii amacrine cell/ON cone bipolar cell (CBC) network. However, it remains unclear whether this hyperactivity reflects changes in the underlying circuitry or dysfunction of the normative circuitry. Here, we used connectomics-based mapping of retinal circuitry to 1) define the coupling architecture of the Aii/ON CBC network in healthy adult rabbit retina using connectome RC1 and 2) evaluate changes in coupling motifs in RPC1, a pathoconnectome from a rabbit retinal degeneration model.
Methods:
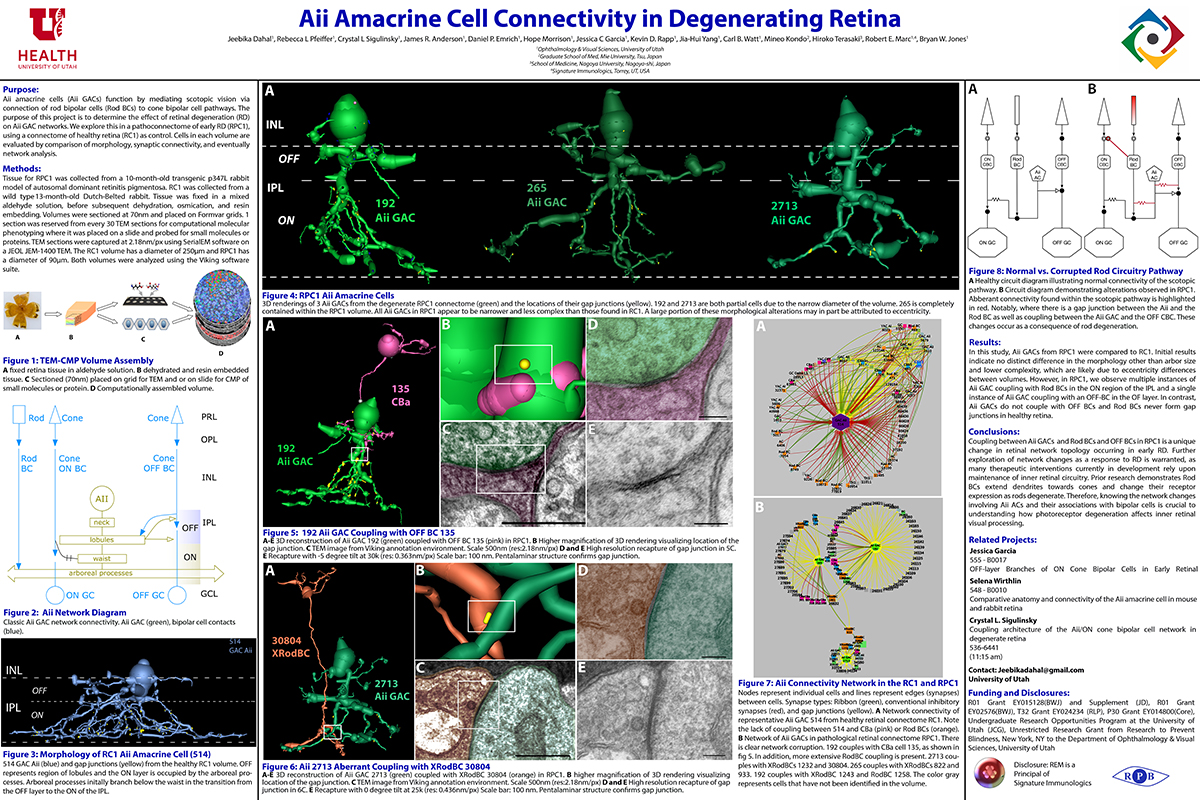
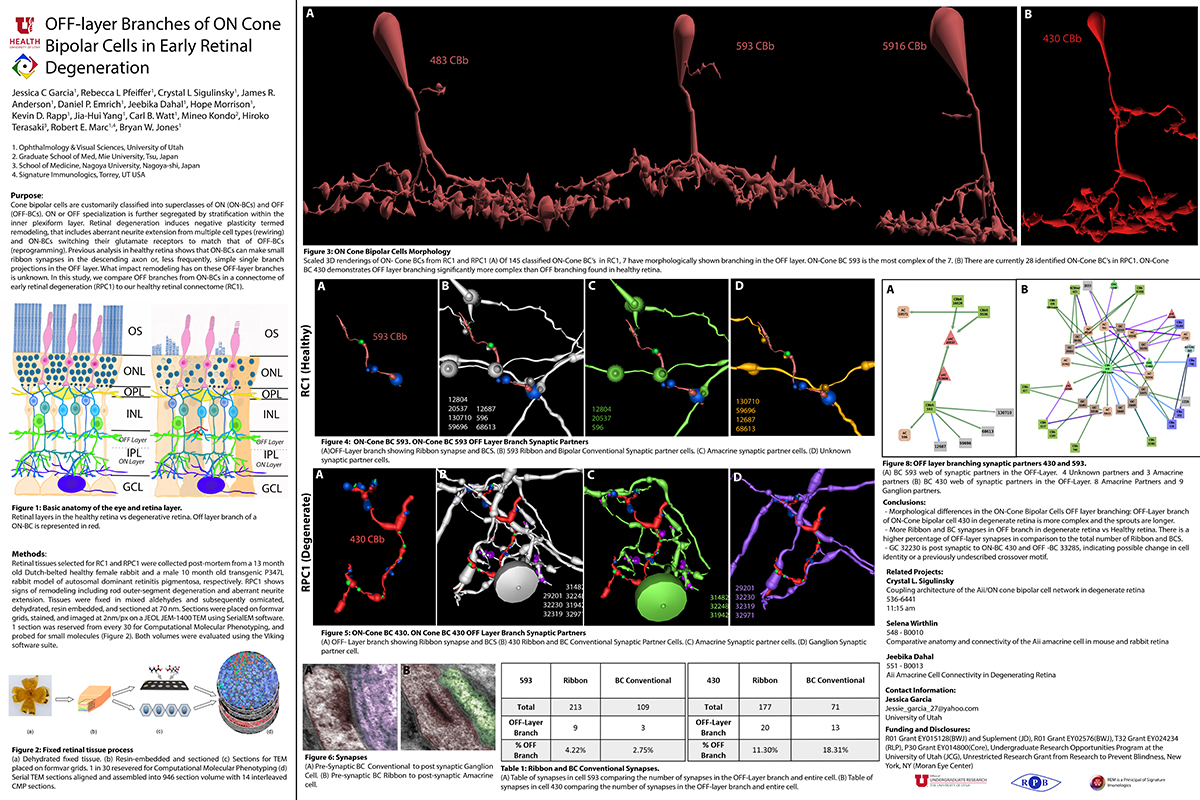
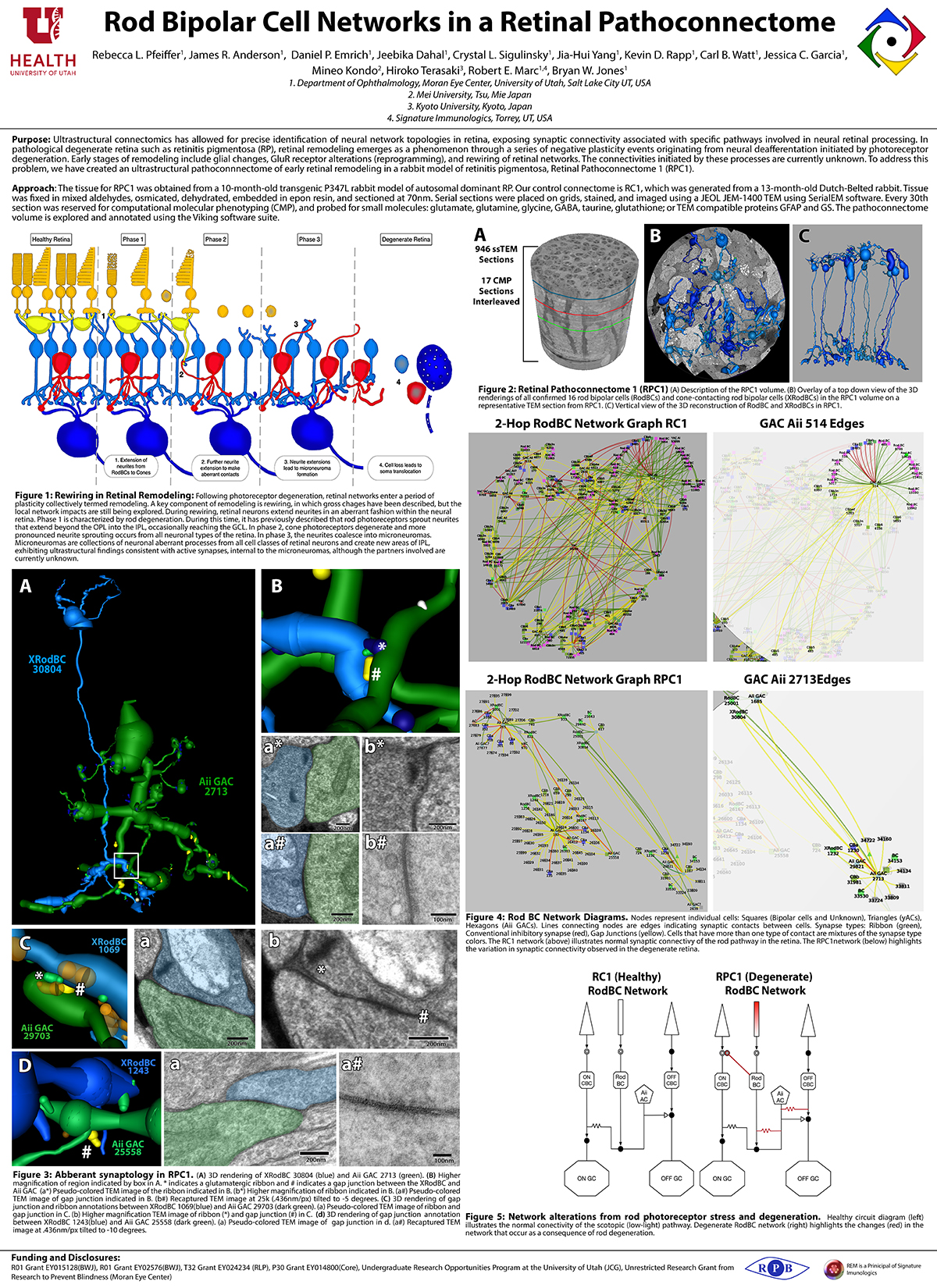
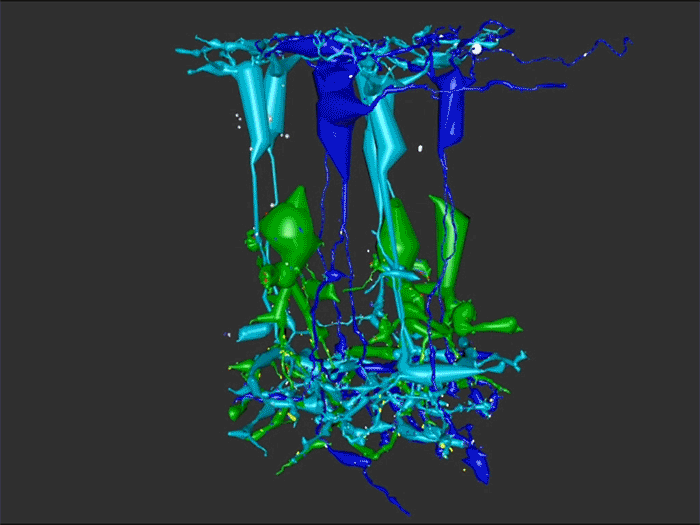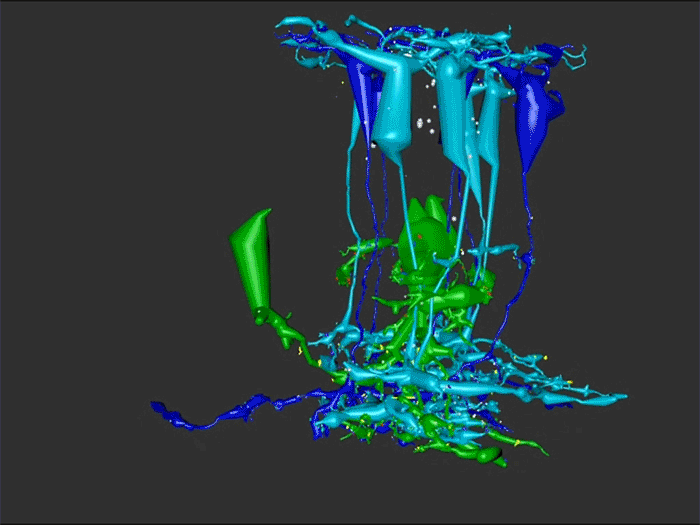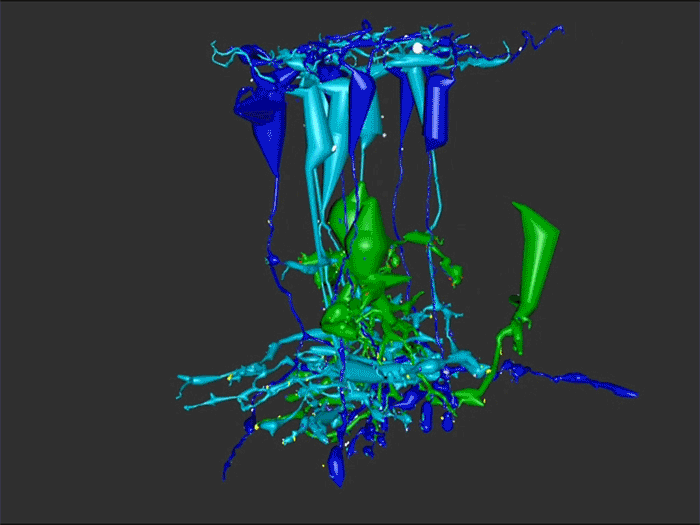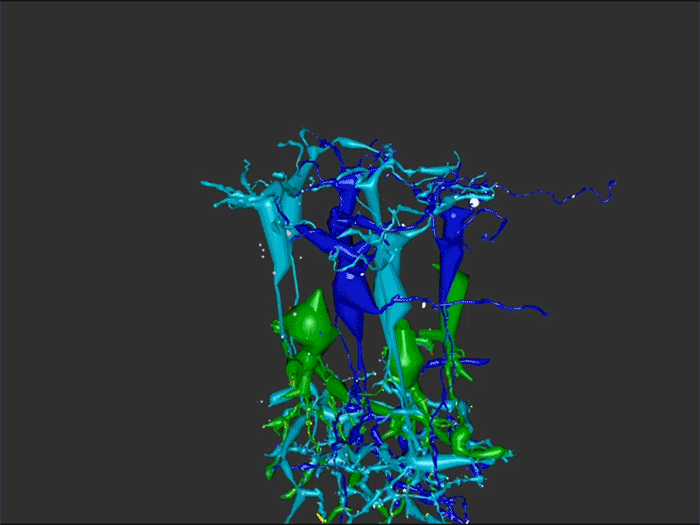
RC1 and RPC1 are connectomes built by automated transmission electron microscopy at ultrastructural (2 nm/pixel) resolution. RC1 is a 0.25 mm diameter volume of retina from a 13-month old, light adapted female Dutch Belted rabbit. RPC1 is a 0.07 mm diameter volume of degenerate retina from a transgenic P347L model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (10-months old, male, New Zealand White background) presenting with ~50% rod loss. ON CBCs, Aii amacrine cells, and their coupling partners were annotated using the Viking application. Coupling motifs and features were explored with 3D rendering and network graph visualization. Gap junctions were validated by 0.25 nm resolution recapture with goniometric tilt when necessary.
Results:
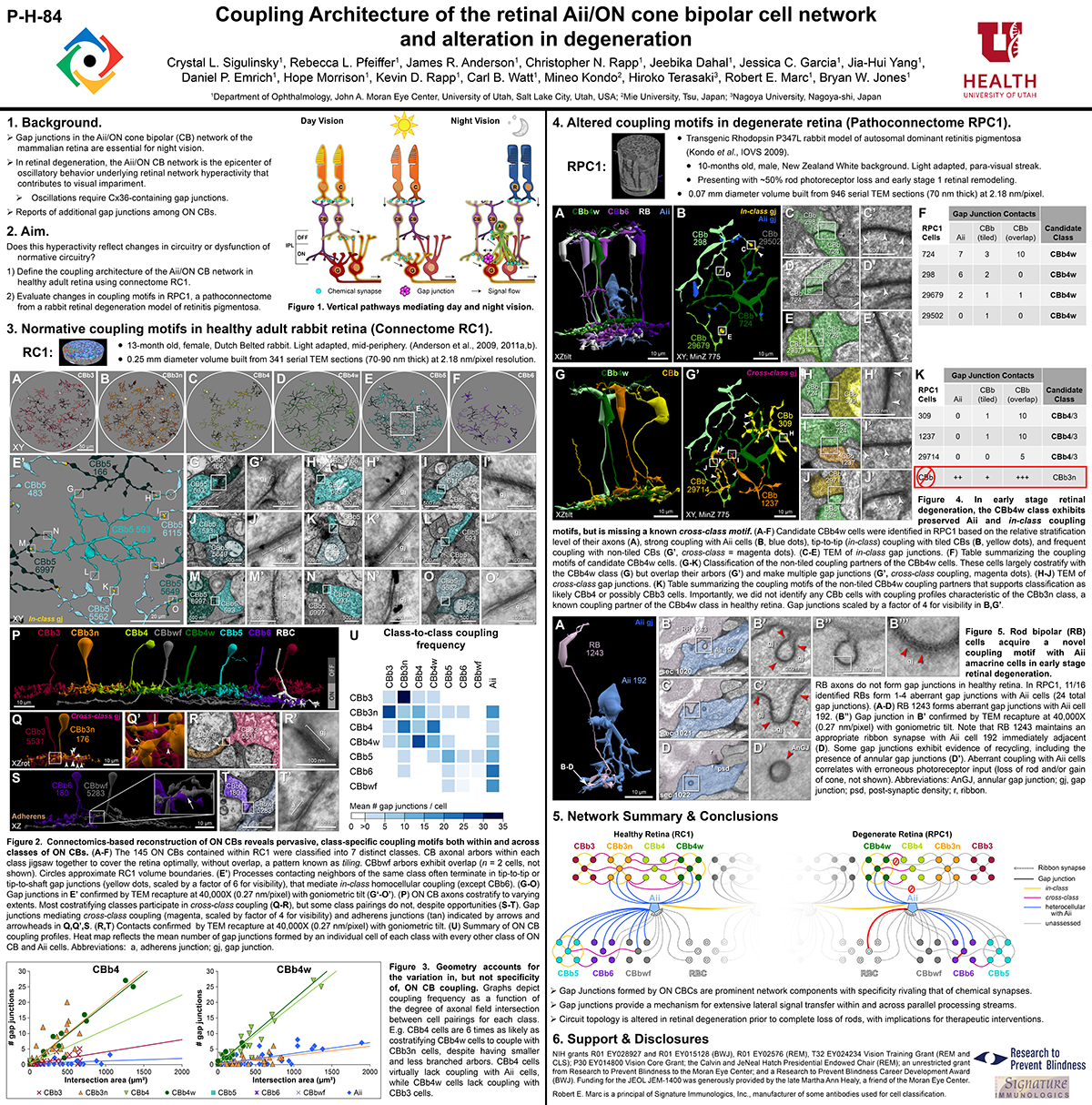
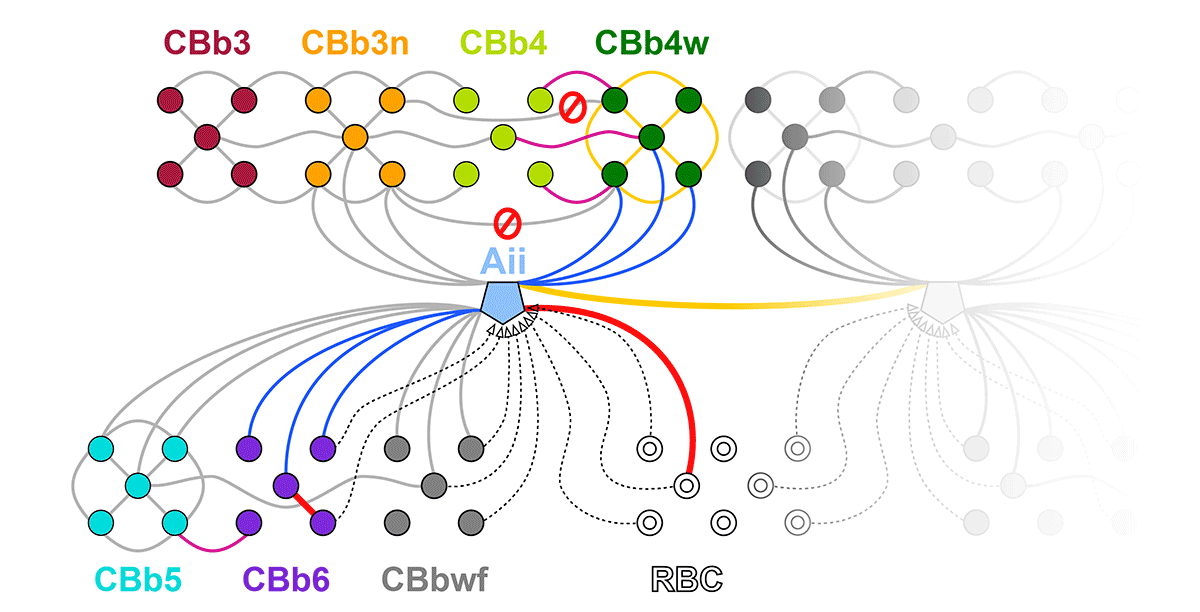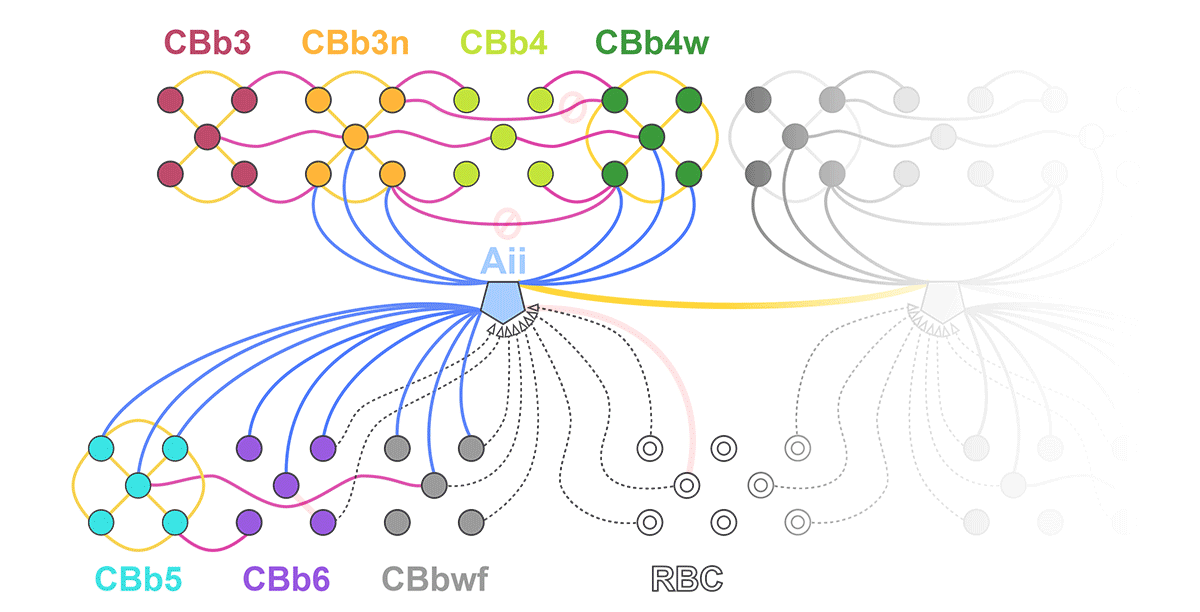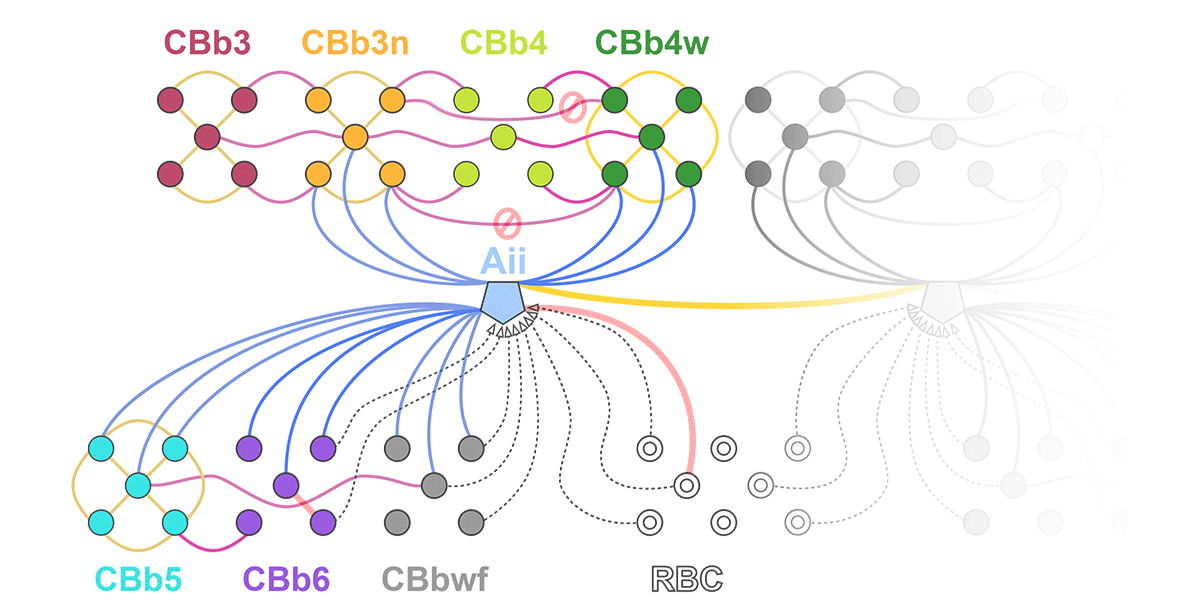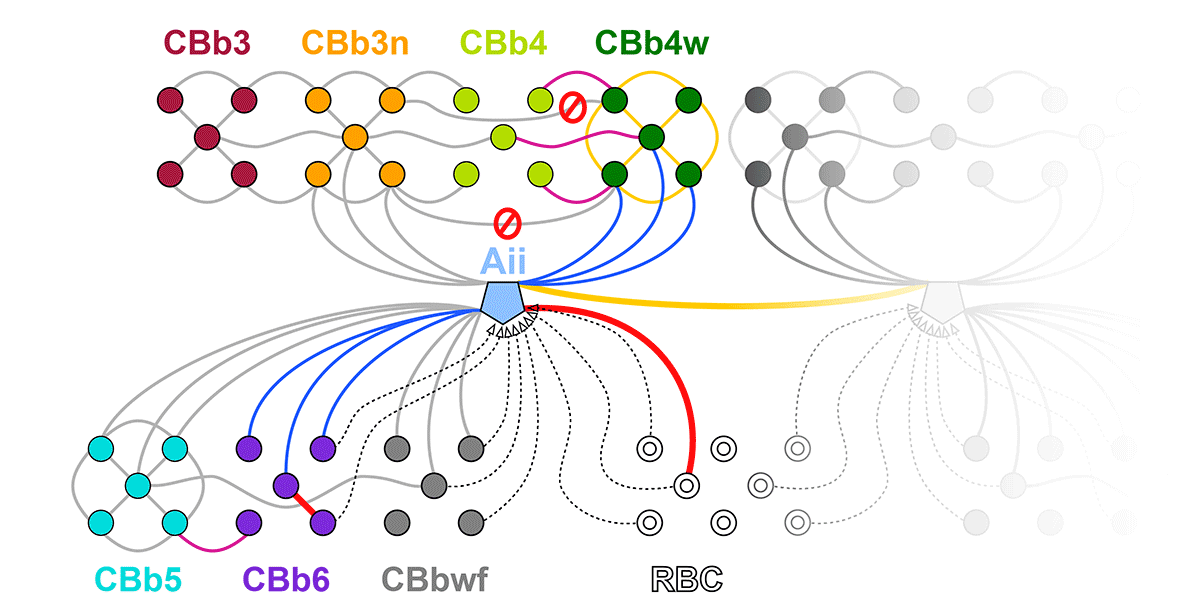
Complete reconstruction of 37 ON CBCs in RC1 yielded 1339 gap junctions and revealed pervasive in- and cross-class coupling motifs among ON CBCs that produce complex network topologies within the coupled Aii network. Robust rulesets underlie class-specific coupling profiles with specificity defined beyond geometric opportunity. These coupling profiles enabled classification of all 145 ON CBCs contained within RC1 into 7 distinct classes. In RPC1, two ON CBC classes appear to retain their class-specific coupling profiles, accepting and rejecting specific combinations of Aii and ON CBC class partnerships. However, aberrant partnerships exist, including both loss of motifs and acquisition of novel ones.
Conclusions:
Gap junctions formed by ON CBCs are prominent network components, with specificity rivaling that of chemical synapses. These gap junctions not only subserve canonical signal transfer for night vision, but also extensive coupling within and across the parallel processing streams. Clearly aberrant morphological and synaptic changes exist in RPC1, including changes in the coupling specificity of both Aii and ON CBCs. Thus, circuit topology is altered prior to complete loss of rods, with substantial implications for therapeutic interventions for blinding diseases that depend upon the surviving retinal network.