We have a new manuscript out in Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, Müller Cell Metabolic Signatures: Evolutionary Conservation and Disruption in Disease.
Authors: Rebecca L. Pfeiffer @BeccaPfeiffer19, Robert E. Marc @robertmarc60, and Bryan William Jones @BWJones.
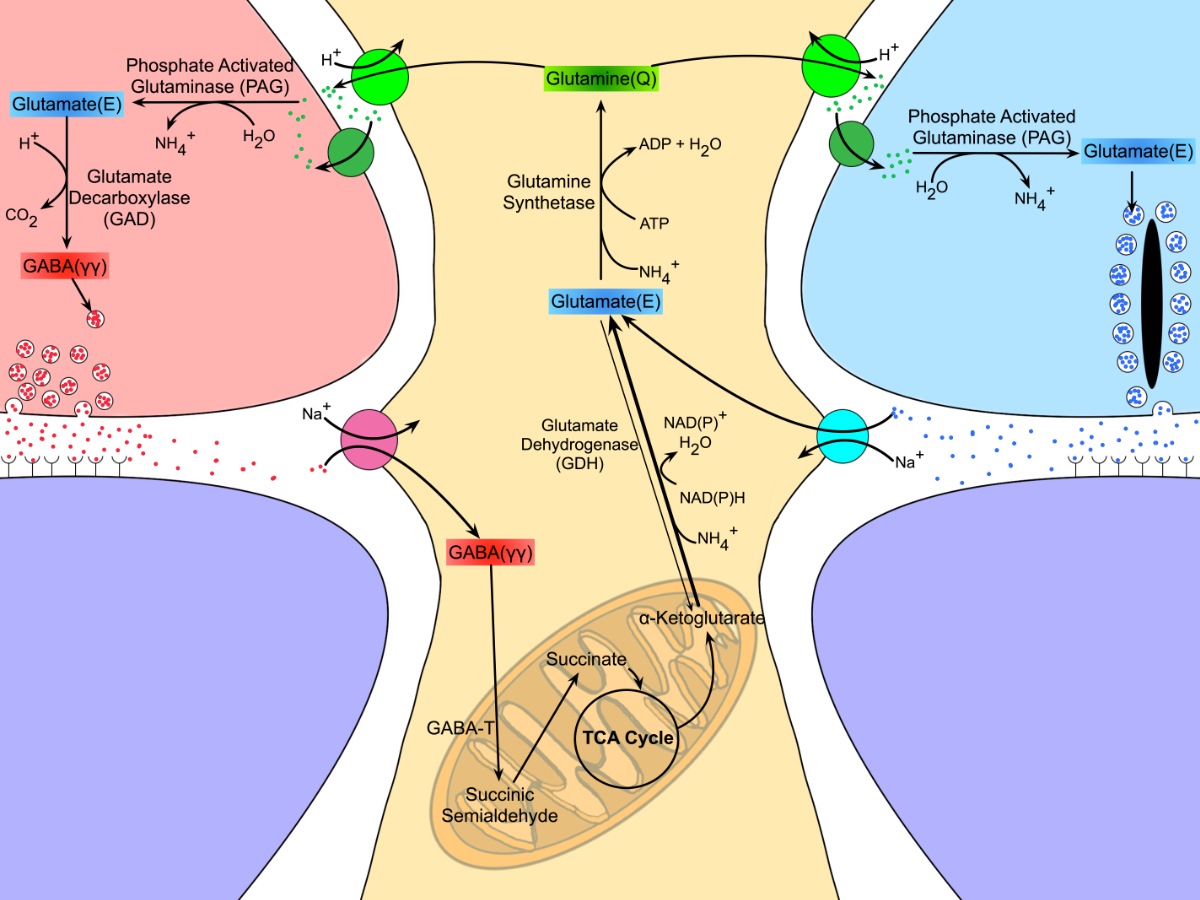
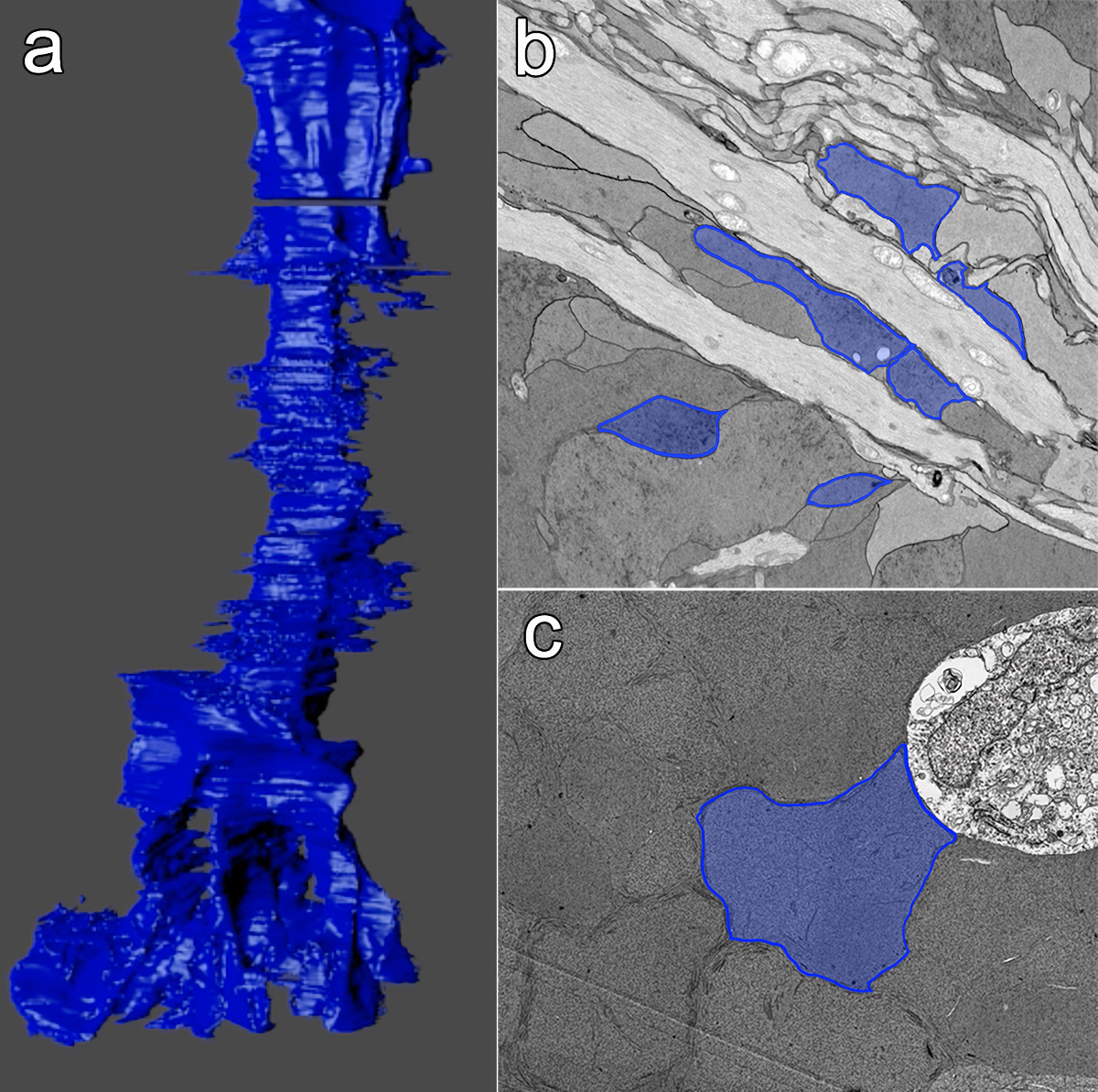
This manuscript functions as both a review and presents some exciting new data demonstrating how the glutamate cycle is disrupted during retinal degenerative disease.
Abstract: Müller cells are glia that play important regulatory roles in retinal metabolism. These roles have been evolutionarily conserved across at least 300 million years. Müller cells have a tightly locked metabolic signature in the healthy retina, which rapidly degrades in response to insult and disease. This variation in metabolic signature occurs in a chaotic fashion, involving some central metabolic pathways. The cause of this divergence of Müller cells, from a single class with a unique metabolic signature to numerous separable metabolic classes, is currently unknown and illuminates potential alternative metabolic pathways that may be revealed in disease. Understanding the impacts of this heterogeneity on degenerate retinas and the implications for the metabolic support of surrounding neurons will be critical to long-term integration of retinal therapeutics for the restoration of visual perception following photoreceptor degeneration.