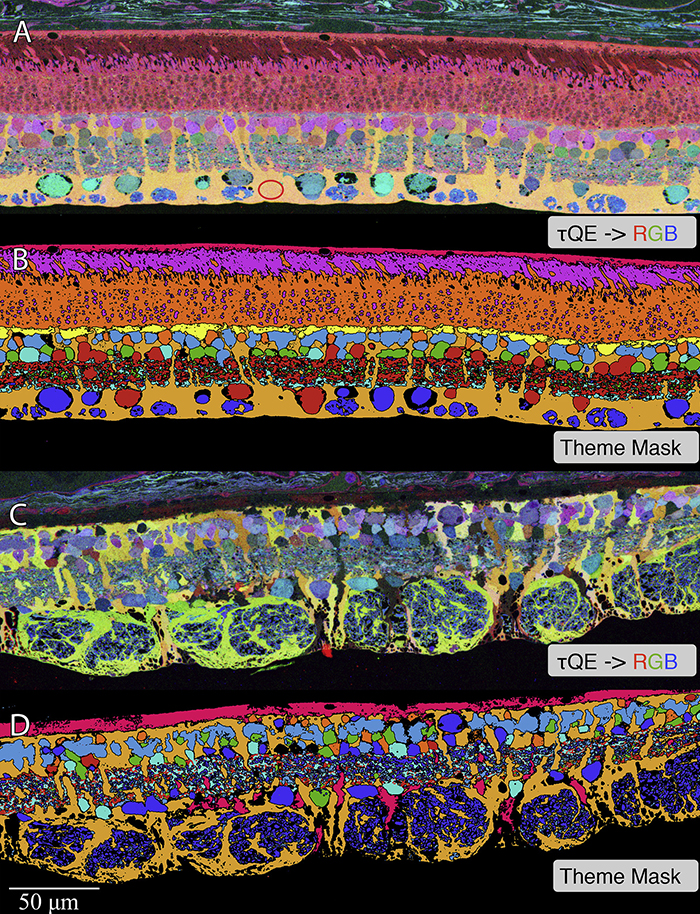
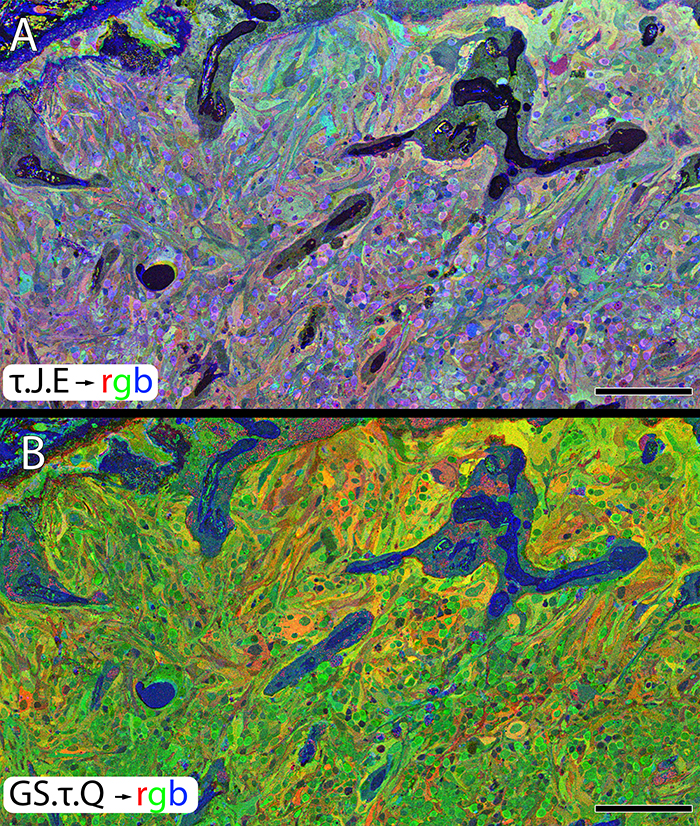
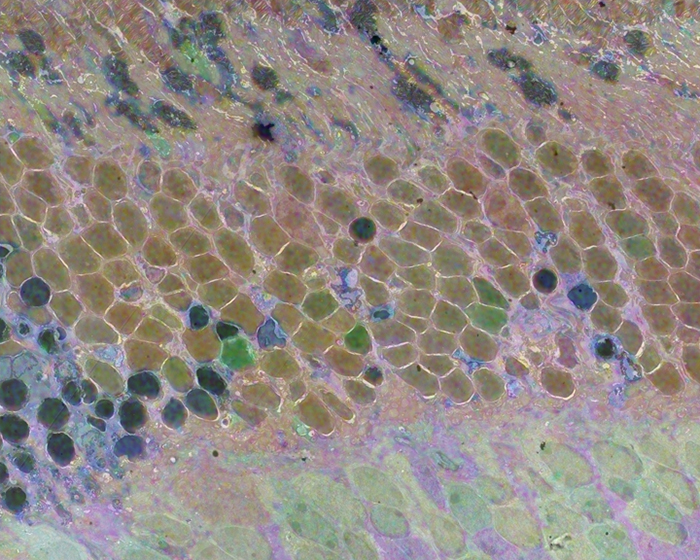
We have a new manuscript from the lab in Experimental Eye Research, (PubMed link here). Metabolic changes and retinal remodeling in Heterozygous CRX mutant cats (CRXRDY/+). This manuscript is in collaboration with the Sheldon Rowan lab out of Tufts University. Authors are: Eloy Bejarano, Elizabeth A Whitcomb, Rebecca L Pfeiffer (@BeccaPfeiffer19), Kristie L Rose, Maria José Asensio, José Antonio Rodríguez-Navarro, Alejandro Ponce-Mora, Antolín Canto, Inma Almansa, Kevin L Schey, Bryan W Jones (@BWJones), Allen Taylor, and Sheldon Rowan (@SheldonRowan). The PDF is here.
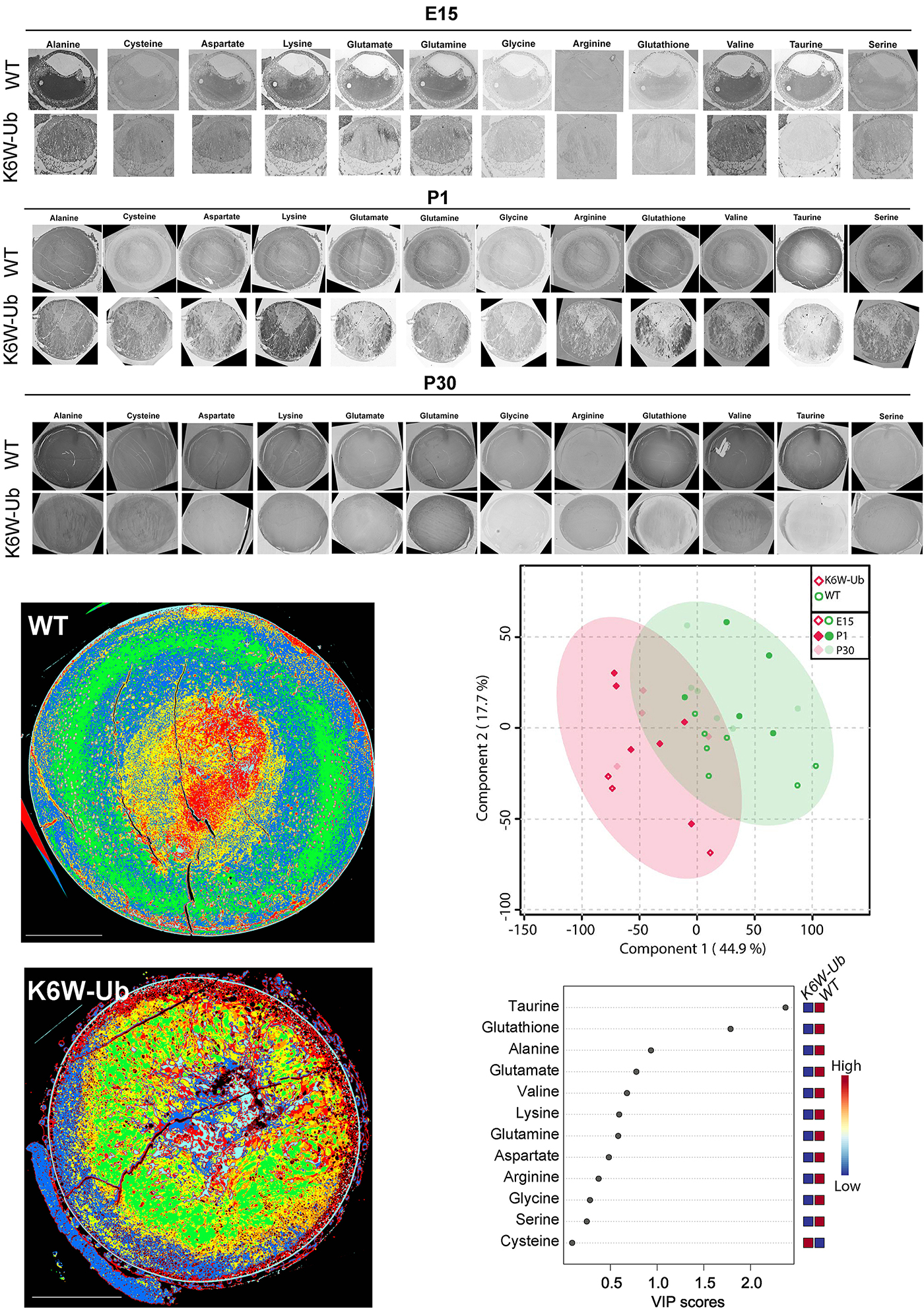
Abstract: The lens proteome undergoes dramatic composition changes during development and maturation. A defective developmental process leads to congenital cataracts that account for about 30% of cases of childhood blindness. Gene mutations are associated with approximately 50% of early-onset forms of lens opacity, with the remainder being of unknown etiology. To gain a better understanding of cataractogenesis, we utilized a transgenic mouse model expressing a mutant ubiquitin protein in the lens (K6W-Ub) that recapitulates most of the early pathological changes seen in human congenital cataracts. We performed mass spectrometry-based tandem-mass-tag quantitative proteomics in E15, P1, and P30 control or K6W-Ub lenses. Our analysis identified targets that are required for early normal differentiation steps and altered in cataractous lenses, particularly metabolic pathways involving glutathione and amino acids. Computational molecular phenotyping revealed that glutathione and taurine were spatially altered in the K6W-Ub cataractous lens. High-performance liquid chromatography revealed that both taurine and the ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione, two indicators of redox status, were differentially compromised in lens biology. In sum, our research documents that dynamic proteome changes in a mouse model of congenital cataracts impact redox biology in lens. Our findings shed light on the molecular mechanisms associated with congenital cataracts and point out that unbalanced redox status due to reduced levels of taurine and glutathione, metabolites already linked to age-related cataract, could be a major underlying mechanism behind lens opacities that appear early in life.