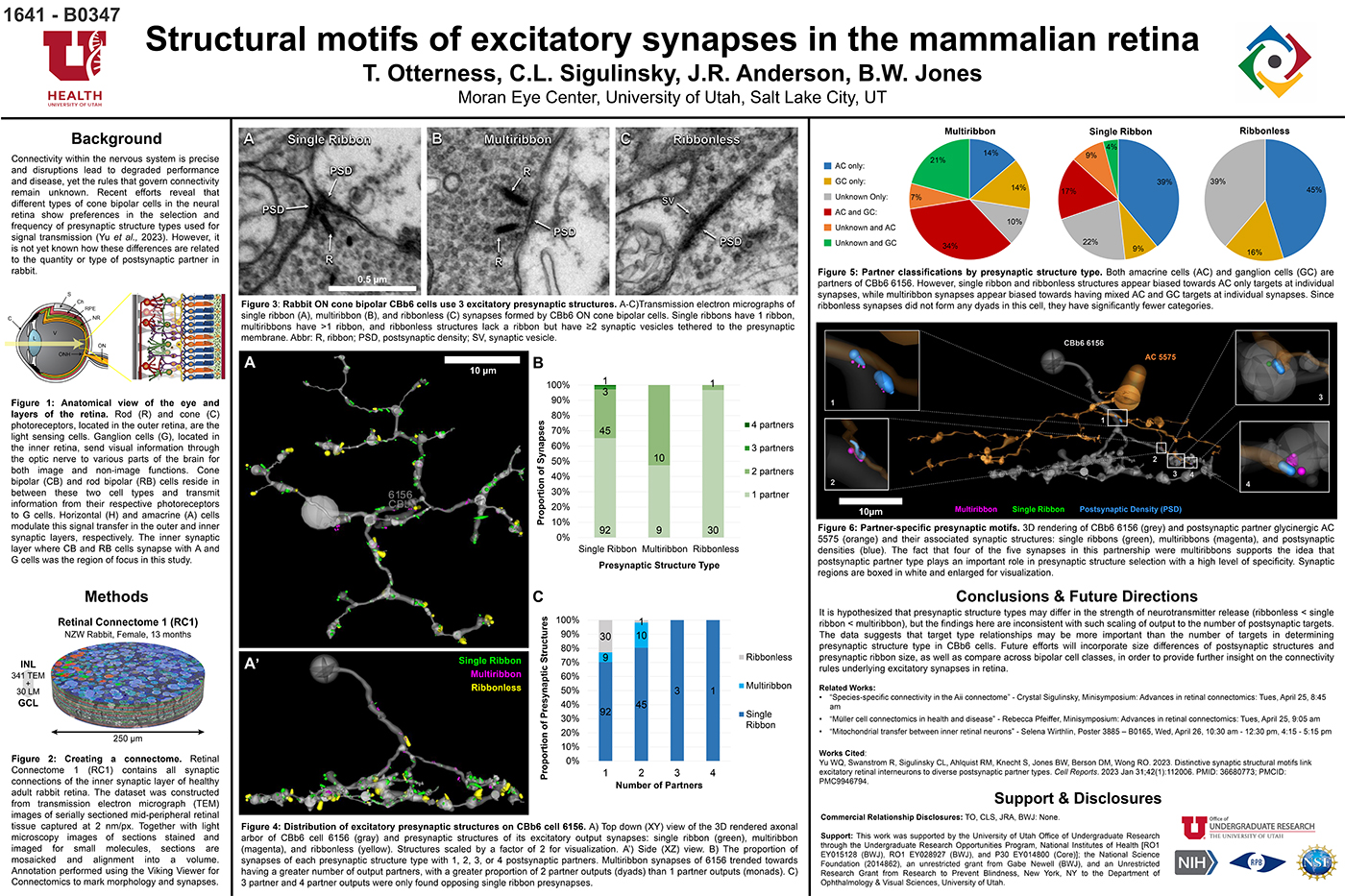
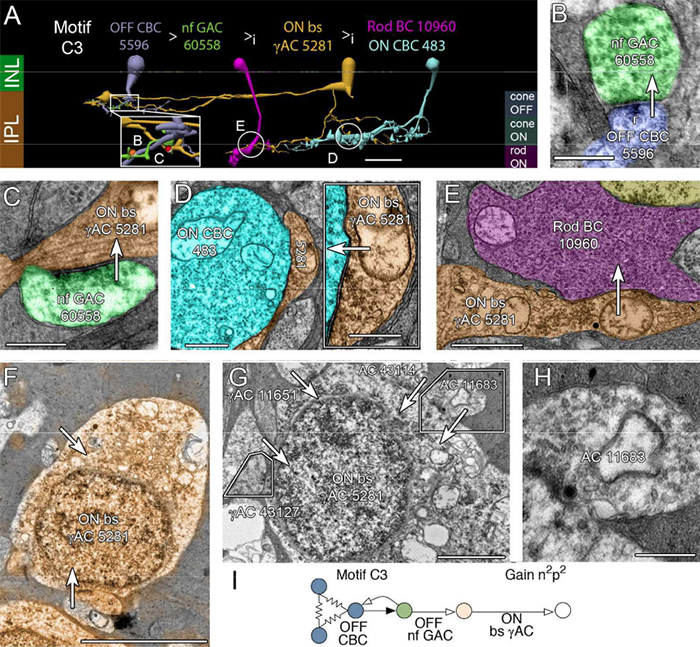
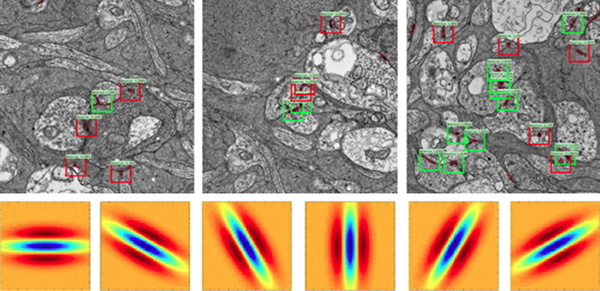
This abstract was presented today, April 26th at the 2023 Association for Research in Vision and Opthalmology (ARVO) meetings in New Orleans, Louisiana by Selena Wirthlin, Crystal Sigulinsky, James Anderson, and Bryan William Jones.
Full resolution version here.
Purpose
Intercellular mitochondrial transfer has been reported across a variety of cells and tissues under both physiological and pathological conditions. Such transfer has shown broad therapeutic potential. The effectiveness of this therapy, however, is limited by a lack of understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms. Here, the ultrastructural features of mitochondrial transfer between inner retinal neurons discovered through retinal connectomics analysis is shown.
Methods
Retinal Connectome 2 (RC2) was built by automated transmission electron microscopy at ultrastructural (2nm/pixel) resolution. RC2 is a 0.25mm diameter volume of retina obtained from a 5-month-old female C57BL/6J mouse. The Viking application was used to visualize and annotate inter- and intracellular features of interest in the connectome.
Results
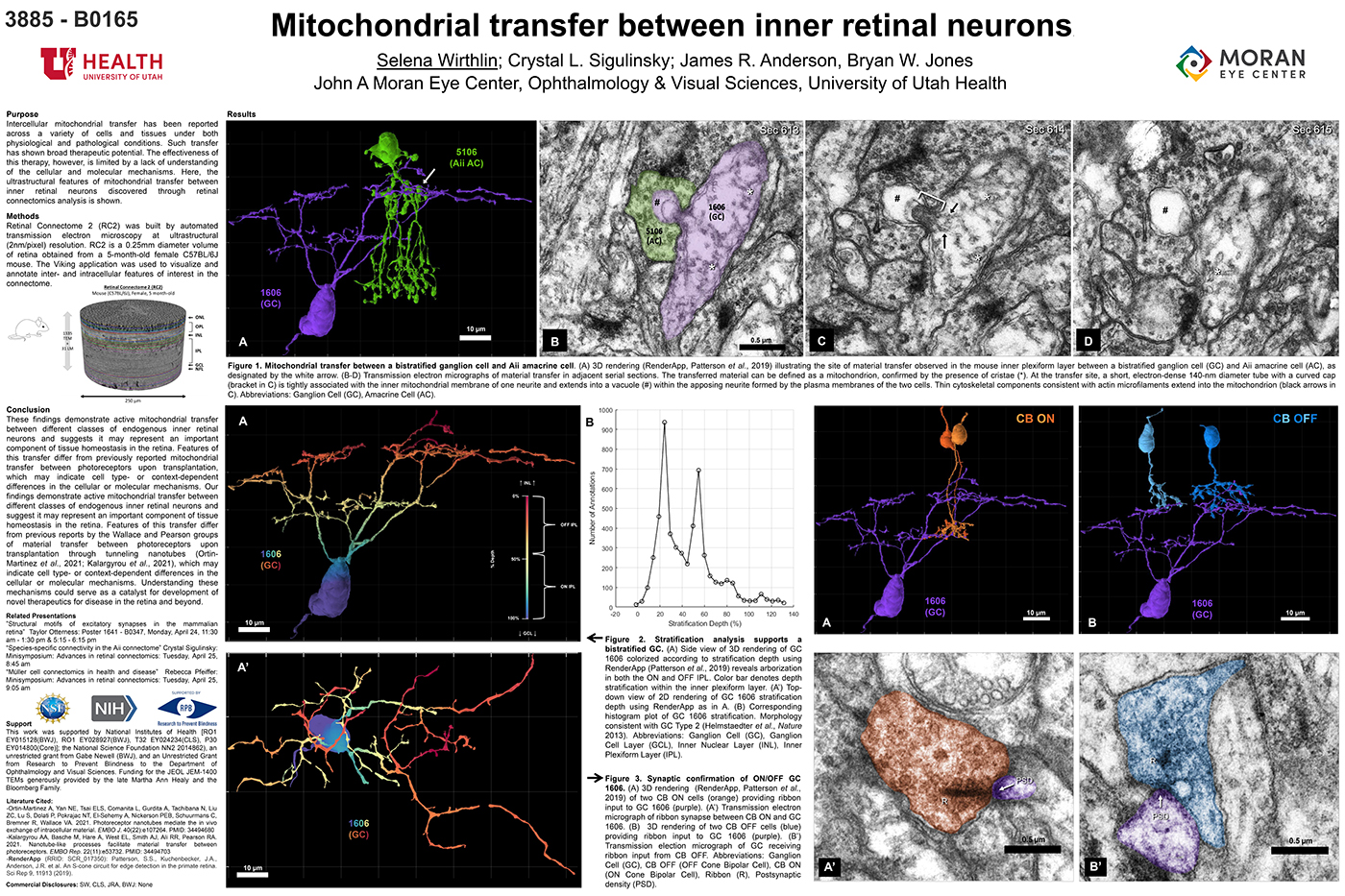
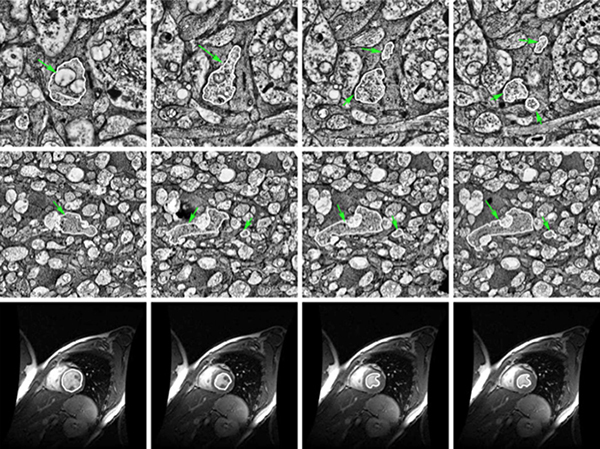
Exploration of RC2 revealed material transfer between apposing neural processes within the OFF subliminal of the inner plexiform layer. The transferred material can be defined as a mitochondria, confirmed by the presence of crustae. At the transfer site, a short, electron-dense 140-nm diameter tube with a curved cap tightly associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane of one neuritis extends into a vacuole within the apposing neuritis formed by the plasma membranes of the two cells. Thin cytoskeletal components consistent with actin microfilaments extend into the mitochondrion. Morphology and synaptology of the acceptor cell confirm it is an Aii amacrine cell, while preliminary findings suggest the donor cell is a type of ON/OFF ganglion cell.
Conclusions
These findings demonstrate active mitochondrial transfer between different classes of endogenous inner retinal neurons and suggests it may represent an important component of tissue homeostasis in the retina. Features of this transfer differ from previously reported mitochondrial transfer between photoreceptors upon transplantation, which may indicate cell type- or context-dependent differences in the cellular or molecular mechanisms. Our findings demonstrate active mitochondrial transfer between different classes of endogenous inner retinal neurons and suggest it may represent an important component of tissue homeostasis in the retina. Features of this transfer differ from previous reports by the Wallace and Pearson groups of material transfer between photoreceptors upon transplantation through tunneling nanotubes (Ortin- Martinez et al., 2021; Kalargyrou et al., 2021), which may indicate cell type- or context-dependent differences in the cellular or molecular mechanisms. Understanding these mechanisms could serve as a catalyst for development of novel therapeutics for disease in the retina and beyond.